
Whether you are a local giant or an entrepreneur, in your quest to get global attention you must have started making preparations for the digital promotions. And while doing this, the most common term that you have come across is SEO (Search Engine Optimization).
Come, let’s learn what is SEO and how it works.
What Is SEO?
In a nutshell, SEO is a process to make your content more presentable to the search engines so that they easily understand what it’s all about and show it to the users when relevant queries are made.
Why Is SEO Important for Your Business?
The higher you rank for a keyword on the search engines, the more opportunity you have to get relevant traffic on your website. So, if you want to increase your sales, the very first thing you want is visitors. And SEO is a process of getting free traffic that can eventually improve your sales.
- What Is SEO?
- Why Is SEO Important for Your Business?
- How Do Search Engines Work?
- What Is the Aim of a Search Engine Algorithm?
- What Happens When a Search Is Performed?
- How Do Search Engines Crawl?
- Different Search Engines and Their Market Share
- Evolution of Google’s Algorithm
- How to Do SEO?
- What Type of Businesses SEO Is Useful For?
- Tools and Software for SEO
- Web’s Best Resources for SEO
- Common KPI’s of a Successful SEO Campaign
- Role of Website Design in SEO
- Conclusion
How Do Search Engines Work?
Every search engine has its own crawler that navigates the web by downloading web pages, following the URLs on these pages with the intention to discover new pages on the web.
The discovered web pages are then added into a data structure called index that includes all the identified URLs along with a number of signals that differentiate the types of content each URL has. These signals are:
- The keywords found throughout the content
- The topics covered by each web page
- The type of information found in microdata or schema
- The publishing date of the content
- The engagement rate or how people interact with the content of the web page
What Is the Aim of a Search Engine Algorithm?
A search engine algorithm always tries to show the most relevant content that can fulfil a user’s search intent as quickly as possible. Based on the user interaction with the list of results, the future ranking of these web pages is determined.
What Happens When a Search Is Performed?
When a search query is made, all the relevant pages are identified from the index and they are ranked using algorithms that are different for every search engine. For example, a web page that ranks on Google, may not get a rank on Bing. Apart from the search query, the search engines use various other data to show a relevant list of results. They are:
Search engines always track the IP address of a device to determine where a search is made from. This helps in providing location-based results when keywords like “restaurants near me” and “movie showtimes” are searched for.
Search engines use your previous search history to provide you customized results.
Search engines also throw results based on the native language of the user.
How Do Search Engines Crawl?
All search engines have their crawlers to find and get details about the web pages. The very first thing that the crawlers do is to download the robots.txt file of a website. It generally contains information about the sitemap and the list of URLs that the site owner wants the search engines to crawl.
There are a good number of algorithms used by the search engines to determine how frequently a website should be crawled and indexed. Generally, the crawl and index rate of a website depends on the frequency of changes made on it.
Crawlers also find new URLs from existing and already indexed pages. These new pages are added to the crawl queue so that they can be downloaded and indexed on a later date. Another way to get indexed is manual submission of links to the search engines. It is normally done if there are some indexing issues faced or if it takes too much time to crawl a URL.
Crawlers cannot read anything other than texts. However, if they encounter URLs containing images and videos, the file name associated with the file and the metadata of the page will be read. Although the search engines can extract a limited amount of information from the files, it will mainly depend on the metadata and filename to rank the particular URL.
How Do the Search Engines Index?
Indexing is a process by which search engines organize all the necessary information before a search so that a fast response can be provided.
Looking into each page for relevant keywords would require a lot of time to process the data and show it in the SERPs. Instead, an inverted index method is used to identify the relevant information. In this process, a database of text elements is compiled along with pointers. Then, a method, named tokenization is used to reduce the texts to their core meaning. In this way, the amount of resources is reduced and a faster process of delivering results against all relevant search queries is developed.
How Do the Search Engines Rank Web Pages?
When a search is performed, search engines look into the index for highly relevant content and then reorders the web pages and show them on SERPs to solve the users’ query. This distribution of web pages is known as ranking.
There are numerous ranking factors like quality content, social engagement, brand authority, good traffic, backlinks, website load speed and more. Among them, backlinks have always been considered as one of the powerful ranking factors. When a web page gets linked with content elsewhere, it is then considered as a vote of confidence and trust. The number of these links and the authority of these websites often determine the PageRank of the linked-to page.
There are ways to restrict search engines from crawling the web pages you don’t want to be indexed. But there should be reasons for doing so. Generally, the pages that require more security like the pages of a banking site, the login pages of a website and especially the emails are generally kept secret. But if you want your web page to be visible to your users, make sure that your robots.txt file does not discourage the search engines.
Different Search Engines and Their Market Share

Based on a report of Stat Counter, the market share of the top search engines, namely Google, Bing, Yahoo, Yandex and Baidu in August 2019 are 92.37%, 2.63%, 1.8%, 1.1% and 0.51% respectively. As Google dominates the web single handedly, we will mostly concentrate on Google’s algorithm and updates to define search engine optimization techniques. Before that, let’s have a look at the basic differences between these search engine algorithms.
Google is focusing more on mobile-first indexing where they give more importance to the performance of the mobile version of a website rather than the desktop version. Google also considers backlinks as a strong ranking signal but it mainly focusses on quality over quantity. When it comes to social signal, Google does not give much importance to the social presence of brands due to the difficulties of understanding social identities that may be incomplete or misleading.
Bing has not yet declared its plan on mobile indexing but it uses the backlink information in much the same way as Google. Strikingly, Bing gives much importance to the social signals which actually is a part of its algorithm.
Yandex claims that they have a mobile-friendly algorithm and started labelling mobile-friendly web pages in their index from November 2015. But unlike Google and Bing, Yandex stopped using backlink data to rank a website. Regarding social signals, there’s still confusion whether Yandex pays enough attention to social presence.
Baidu throws different search results when different devices are used. It is also noteworthy that the dominant search engine of China uses a transcoding technique to convert non-mobile-friendly web pages to Baidu-generated web pages that work perfectly on mobile devices.
Evolution of Google’s Algorithm
Though Google was officially launched in 1998, it took 2 years to launch its first algorithm update. No record of algorithms is found between 1998 to 2000. They started introducing algorithmic updates from 2000 to deliver more useful content to the users and to restrict spammy activities.
Here’s a brief history of the algorithmic updates we witnessed from 2000.
- 2000 Updates
Google launched a browser toolbar in the year 2000. It was a plugin to help users search for information fast from any web page. It also came with the feature to locate phrases on any web page without web browsers “find” feature.
- 2002 Updates
Though Google has never declared any algorithmic update in 2002, some major rank drops were witnessed by the then webmasters. To get some idea about the update, check out the discussion here.
- 2003 Updates
This was the year when webmasters witnessed a lot of updates (both confirmed and unconfirmed) in a very short time.
On February 1, 2003, Google introduced SES Boston which was aimed at major monthly updates.
Cassandra was announced on April 1, 2003 in order to solve the link-quality issues. It was mostly focussed on identifying and banning the co-owned domains.
Another unconfirmed update, namely Dominic was announced on May 1, 2003, to make a proper count of the backlinks that a website has.
The monthly Google Dance came to an end on July 1, 2003, with the Fritz update that changed the indexing process.
Finally, on November 1, 2003, Google introduced Florida that determined the future of SEO industry. Many site owners became furious because of massive rank drops and it was the end of practicing low-quality late 90s tactics like keyword stuffing. - 2004 Updates
Austin, the unconfirmed update of Google, came into action on January 1, 2004. It was basically an upgraded version of Florida that continued identifying the spammy on-page tactics.
The Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) was first introduced through Brandy which was announced on February 1, 2004. It was one of the most futuristic updates of Google as it increased the attention to anchor texts and made it easy for Google to understand the synonyms. - 2005 Updates
On January 1, 2005, the “nofollow” attribution was jointly introduced by Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft with an aim to control the quality of outbound links. Though it was not a traditional Google update, it certainly had a significant impact on the link graph.
On May 1, 2005, Bourbon was announced and it primarily focused on identifying the duplicate content and non-canonical URLs. Google’s previous attempts of personalization required custom settings and profile but 2005’s personalized search started understanding user’s search history and automatically adjusted results.
From June 1, 2005, Google started allowing webmasters to manually submit XML Sitemaps using webmaster tools.
Jagger, another update to control link spams like reciprocal links, paid links and link farms was rolled out on October 1, 2005.
Google merged its maps data into the previously created Local Business Center also on October 1, 2005, and it eventually made a number of changes in Local SEO.
On December 1, 2005, the much-awaited update, Big Daddy was announced. It was primarily an infrastructure update that took care of URL canonicalization, redirects and several technical issues. - 2006 Updates
No major updates were witnessed in the year 2006. Apart from some ranking changes, Google continued to make alterations to the supplemental index throughout the year.
- 2007 Updates
There were two noticeable updates in 2007. Webmasters do not have much information about the unconfirmed Buffy update which was rolled out on 1 June 2007.
The other one, namely Universal Search which got released on May 1, 2007, was not a typical algorithm update. It actually added news, videos, images, local and other verticals with the traditional search results. - 2008 Updates
Along with a minor update, Dewey, the year 2008 witnesses Google Suggest, one of the biggest updates of all time. It introduced suggested searches in a drop down below the search box as soon as the visitors start typing a search query.
- 2009 Updates
On February 1, 2009, Google, Microsoft and Yahoo jointly declared Canonical Tag so that the webmasters can send canonicalization signals to the bots without affecting human views.
Vince, the unconfirmed update was also released on February 1, 2009. Though webmaster complained that Google seemed to favour big brands after this update, it was later declared as a minor change.
Another major update declared on December 1, 2009, was Real-Time-Search which integrated Twitter feeds, Google News and several newly indexed content into the real-time feed on the SERPs. - 2010 Updates
The Places page was released in September 2019 but it was still a part of Google Maps.
Google Places was officially launched on April 01, 2010 with a number of new features, including the options to advertise locally.
Between April and early May 2010, webmasters started noticing massive rank drops in long-term searches. It was later declared by Matt Cutts that there was an algorithmic change that impacted websites with thin content.
On June 1, 2010, Google rolled out the Caffeine update that boosted the raw speed of Google and made the crawling and indexation much accurate.
The highly anticipated update, Google Instant was launched on September 1, 2010. It made the search results visible to the users as soon as the query is typed.
Instant previews were launched on November 1, 2010, enabling users to have a quick preview of the landing pages from the search results.
In 2010, the New York Times covered the news of how Décor My Eyes, an eCommerce site got rank based on the negative reviews. After this, Google made slight changes to the algorithm to identify websites following this tactic. - 2011 Updates
To restrict the profile scams, the Attribution update was rolled out on January 28, 2011, to differentiate content attribution in a much better way.
On February 23, 2011, a major update, Panda hit websites hard, affecting nearly 12% of search results. The update played an effective role against websites with thin content, high ad-to-content ratios and link farms.
To compete with the major social media channels like Facebook and Twitter, Google rolled out the +1 button next to the links. It was similar to the ‘Like’ button of Facebook added with the intention to identify the search results that users like and based on the linking of the users, the ranking of a particular website would increase.
Panda 2.0 was introduced on April 11, 2011, affecting all English queries worldwide (not restricted to the English-speaking Countries).
On June 2, 2011, Google, Yahoo and Microsoft jointly supported structured data and created a number of schemas to produce richer search results.
Google continued to update Panda and launched Panda 2.2 on June 21, 2011. Since then, webmasters started considering Panda as a major ranking factor.
Google came into direct competition with the social media channels with the launch of Google + on June 28, 2011. As it was integrated with the other Google products, it was never difficult to get users for the newly released social media site and within two weeks Google + managed to get two million users.
Panda 2.3 was introduced on July 23, 2011, with some minor changes in the Panda data and on August 12, 2011, Panda 2.4 was released internationally both for English-language-queries and non-English-language queries except Chinese, Japanese and Korean. It affected 6-9% queries internationally.
On August 16, 2011, Google launched expanded site links for brand queries. It was 12 packs at the time of launching but later it was reduced to 6.
Before the pagination update, there was a huge error in crawl and identification of duplicate content. To fix this issue, Google introduced rel = “next” and rel = “prev” attributes on September 15, 2011.
After one month, Google rolled out another Panda update. The details of Panda 2.5 were not clear but some websites were reported to have a huge impact after this update.
The “not provided data” we find in the Google Analytics report is due to the Query Encryption update released on October 8, 2011, as Google started encrypting search queries for privacy reasons.
On November 3, 2011, Google came with the Freshness update that emphasized more on the recent content published online. After Panda 2.5, Google started Panda Flux where updates took place more frequently in minor forms. - 2012 Updates
The very first update webmasters witnessed in 2012 was January 30-Pack where Google announced 30 changes that include image search, more relevant website links, more rich snippets and relevant query improvements.
Right after the release of January 30-Pack on January 5, 2012, Search + You, World update was rolled out where Google emphasized a radical shift in customization and pushed Google + profiles aggressively into the SERPs.
On January 19, 2012, Google came with Ads Above The Fold update to restrict the webpages that have too much ad space.
The second set of “search quality highlights” was published on February 27, 2012. It claimed more than 40 changes that include image-search updates, freshness update and Panda update.
Venice, a part of the monthly update was released on February 27, 2012. This update was aimed at localizing organic search results and adding more localized data.
Another set of 50 updates was rolled out on April 3, 2012. It included Panda 3.4, alterations to anchor-text scoring, image search results and more.
The famous Penguin update, also known as Webspam Update was rolled on April 24, 2012. It adjusted many spam factors that include keyword stuffing and it got an effect on 3.1% of searches made in English language.
On May 4, 2012, Google released April 52-Pack where the details of 52 updates in April were published.
Google Knowledge Graph which became live on May 16, 2012, was one of the biggest steps toward semantic search. It was an SERP-integrated exhibition of the additional details about people, places and things.
Penguin 1.1 was launched on May 25, 2012, and it confirmed that the Penguin data was being processed outside the main search index.
On June 7, 2012, Google published the May 39-Pack that came with Penguin improvements, better ways to detect link schemes, amendments to snippets and updates to Google News.
The month of June witnessed another Panda update where Google claimed that less than 1% of search results were affected but according to the ranking report, the impact was more significant than the previous Panda updates. It was released on June 25, 2012.
A month after (July 24, 2012), Google launched another Panda Update, due to which, rankings fluctuated for about a week.
On August 10, 2012, Google declared that they would start penalizing the websites that have violated the copyright policy repeatedly via DMCA take down requests.
Google changed its way of dealing with the EMDs with the Exact Match Domain update released on September 27, 2012. Due to this update, the presence of EMDs got affected in the MozCast data set by over 10%.
Another update released on September 27, 2012, was Panda #20 which was both Algo + Data update, affecting 2.4% of search queries.
On October 9, 2012, the Page Layout Update #2 was rolled out. Like the previous Page Layout Update, it also targeted pages with an excessive number of ads above the fold.
Google expanded Knowledge Graph functionalities to more languages like Spanish, French, Portuguese, Japanese, Russian and Italian on December 4, 2012.
The year ended with another Panda Update on December 21, 2012. It was called an official refresh, affecting 1.3% of English language search queries. - 2013 Updates
The first official update of Google was Panda #24, affecting 1.2% of search queries.
To restrict domain crowding diversity, Google released an update on May 2013. The timing is not confirmed but it is guessed that it was rolled out just prior to penguin 2.0.
The much-awaited Penguin 2.0 was released on May 22, 2013, with some minor changes. Though its exact impact is unconfirmed, but the reports suggest that the update was mainly targeted to the page level.
On June 11, 2013, Google published an algorithm targeting niche sites having huge spammy activities. The update mainly impacted on porn and loan websites.
Google confirmed the Panda Recovery update on July 18, 2013. Though the exact nature of the update was unclear, webmasters guessed that it softened the previous Panda penalties.
The in-depth Articles update, released on August 6, 2013, was one of the major content updates released by Google. It was primarily added in the news result to encourage evergreen, long-form content.
However, now long-form content can be found in the normal search results and webmasters also encourage writing long-form content.
Another highly discussed update, named Hummingbird was announced on August 20, 2013. Hummingbird is often compared to Caffeine and considered a major algorithmic update that affected semantic searches and Knowledge Graph.
Penguin 2.1 is the last confirmed update released by Google in the year 2013. It was announced on October 4 and was basically a data update, resulting in some minor changes in Google’s algorithm. - 2014 Updates
Google’s page layout algorithm was changed on February 6, 2014, and this resulted in the launch of Page Layout Update #3. The update was mainly focussed on identifying and penalizing the websites with too many ads above the fold.
Google updated their Payday Loan algorithm to restrict spammy queries on May 16, 2014.
Another major Panda Update, Panda 4.0 was launched on May 19, 2014, affecting almost 7.5% English search queries.
On June 28, 2014, all authorship photos were started dropping from the search results with the Authorship Photo Drop update.
On July 24, 2014, the local businesses were shocked by the dramatic alterations in the local search results as the Pigeon was released. According to the official statement, Pigeon created closer relationships with the local and core algorithm and it mainly dealt with the location cues.
Google declared on August 6, 2014, that they would be giving preference to sites that are secure and that integrating SSL would be a lightweight boost to the ranking improvement.
From August 28, 2014, Google started removing the authorship markup and stopped processing it. The very next day, the authorship bylines were disappeared from the search results.
Google launched In The News Box update on October 1, 2014, making some minor changes to the news box results and expanding the news links with a longer list of potential websites.
After two years of the original DMCA/ Pirate update, Google released Pirate 2.0 to protect the software and digital media security. This update caused a huge rank drop to a small group of websites.
Pigeon, Google’s one of the major local algorithm updates was launched in the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia on December 22, 2014 after it hit the USA on July 22, 2014. - 2015 Updates
Google announced that mobile rankings would change based on the websites that are mobile-friendly on April 21, 2015, and the Mobilegeddon update started hitting websites from April 22, 2015.
On May 3, 2015, Google acknowledged a major algorithm change, affecting quality signals. Webmasters experienced a broad effect after this update but officially, there was no explanation about the specifics or the nature of the update.
On October 26, 2015, Google announced that machine learning has been a part of the algorithm for a long while and it is the 3rd most important ranking factor. It was just an announcement and the reports suggest that the update was launched in Spring, 2015. - 2016 Updates
A major change to Google AdWords, namely AdWords Shakeup was launched on February 23, 2016, removing the right column ads and placing 4-ad top blocks for most of the commercial searches. It was a significant change as both paid and organic CTR differed a lot, especially for highly competitive keywords.
Google rolled out another ranking signal boost for the websites that perform well on mobile devices. According to the reports, the majority of websites were transformed into responsive websites right after the Mobile-friendly #2 update on May 12, 2016.
Penguin 4.0 was announced on September 23, 2016. It was a major Penguin update as it was in real-time since then.
Between 22-23 September the first phase of Penguin 4.0 which started devaluing bad links rather than penalizing them was witnessed between 22-23 September. Webmasters are not sure about phase 2 but seemingly it was the reversal of earlier Penguin penalties. - 2017 Updates
Google started penalizing websites with too many pop-ups as they damaged mobile user experience. The update is known as Intrusive Interstitial Penalty which was rolled out on January 10, 2017.
A MozCast report released on April 16, 2017, showed that almost half of Page 1 Google results were secure and by the end of the year, it increased to 75%.
On June 20, 2017, the official job portal of Google was launched. It includes a stand-alone 3-pack of job listings in the SERPs, drawn out of all the major job portals like Glassdoor, LinkedIn, Monster etc.
On October 17, 2017, Google launched Chrome 62 that started warning users not to share details with unsecured forms. Though it was not an algorithm update, it was a strong step of Google towards emphasizing the necessity of HTTPS.
Two years of testing for longer snippets caused the increase in the length of meta description character limit from 155 to 300 characters. The update was launched on November 30, 2017. - 2018 Updates
From March 18, 2018, Google started showing zero organic results on a small set of cards that include time, date and queries. It became visible on the SERPs only for one week but webmasters believed that it was a significant sign of things to come.
Google’s first announcement of mobile-first indexing was made on March 26, 2018. They also suggested that they were migrating websites gradually but webmasters were not certain of the impact that this update was about to bring.
On April 17, 2018, MozCast identified a heavy flux of algorithm that continued for almost one week. Google confirmed the update later but did not provide any detail.
Google reduced the snippet length to 150 – 160 characters on May 13, 2018, after testing longer snippets for several months.
From June 14, 2018, Google started removing videos from organic search results and created video carousels. With this, the number of SERPs with videos also increased significantly.
It took a long while to launch mobile speed update after Google officially announced it. According to Google, the update was meant to affect the slowest mobile sites but no major ranking changes were observed due to this.
After warning users of unsecured websites, Chrome 68 started marking non-HTTPS as “not secure” from July 24, 2018.
Another major update that impacted the sites in health and wellness vertical was confirmed by Google on August 1, 2018. - 2019 Updates
The very first update confirmed by Google in 2019 was Deindexing Bug, released on April 5, 2019. According to Moz Data, rank drop of about 4% was witnessed on 5th and 7th April but the affected websites recovered soon.
On May 23, 2019, Google confirmed indexing bugs that started restricting newly published content from getting indexed perfectly.
Google pre-announced “site diversity” update that would restrict sites with more than one listing on SERPs. It was rolled out on June 6, 2019 but according to Moz Data, the impact was relatively small.
How to Do SEO?
Now, this is a very interesting question as there’s no definite way to get into the top ten of the SERPs. It mainly depends on the type of industry and competitors that decide the marketing strategy of a business. However, there are some basic SEO processes that a business owner can follow to increase visibility and organic traffic for website. Please scroll down to learn more.
Keyword Analysis
Keyword analysis is the first step in SEO. Before you start optimizing your website, you must know the phrases that people often use to search products or services you sell. To do it, you should sign up for Google AdWords account and go to Tools > Keyword Planner.
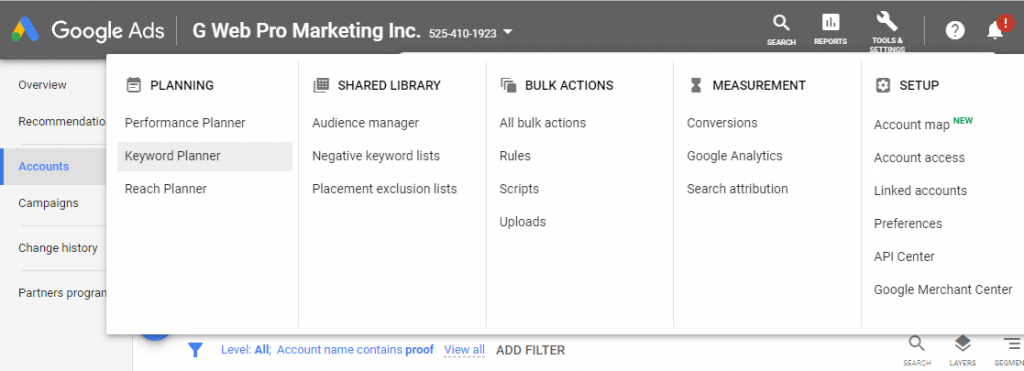
Then you should select the “Discover New Keywords” option.

Then enter the products and services you sell and click on the “Get Results” button.

You will get the ideas of keywords that people often use to make searches related to your products and services. If you are a local business and want local keywords, you can also change the location setting and enter the name of your city by clicking on the location option on top.

You will get a lot of keyword ideas along with several other metrics among which you will need to know the average monthly searches and competition of each keyword for search engine optimization.

The average monthly searches indicate the number of times people in a particular location search for the keyword and the competition signifies how businesses in your industry are paying Google Ads to get ranked in the SERPs. So, if a keyword has high competition, you can easily conclude that it is a money keyword.
So, should you choose keywords that have both high competition and high search volume? The answer is no as there are businesses that are credible enough to defeat you if you are new to SEO. Rather, you should look for keywords that have low to medium competition. The ideal keywords would be those that have low to medium competition but high search volume as they would provide you maximum results with minimum output.
Another important factor you must consider while doing keyword analysis is the search results for a keyword. Just make a Google search with a keyword and see how many results are there on the SERP. It would also give you an idea about the competition that you have to face to rank a keyword.
Now that you have some idea about keywords, you can also check the keywords your competitors are targeting. Just make a Google search with a keyword of your choice and check the title and meta description of the competitors. Just press ctrl+u after visiting the landing page of your competitor and find “title” and “description”. You will come to know which keywords they have used.
The above process will definitely give you some keyword ideas and will help you set your primary keywords.
Keyword Implementation
Now that you are done with selecting keywords for your business, it’s time to integrate them on your website. The very first thing you should do is to write a concise, meaningful and catchy title of 60 characters. and elaborate the title in a description of160 characters. Try to put the important keywords in the title and the other keywords in the description. If you try to keep all the keywords individually in the write-ups, it would result in the repetition of the same words several times. Instead of that, you should write the title and description in a way that covers all the words of every single keyword.
While crawling a web page, Google bots hit the title and meta description at first. Next, you need to add keywords to the headings and subheadings of the landing page. The most important keyword should be added in the H1, and other keywords should also be there in the H2s and H3s. When it comes to the body content, you should include keywords targeted for other pages and hyperlink them with relevant page URLs so that the link juice can flow from one page to another. Even, the URLs of the inner pages must also include keywords. But you have to make sure that the URLs are short and meaningful.
Competitor Analysis

Credits: https://gph.is/1865Asc
Another important task to start your SEO journey is to have an in-depth analysis of your competitors. To do this, you might need both free and paid tools to understand which factors can help get a website to the top positions. Page speed, on-page optimizations, backlinks, domain authority, referring domains, domain age and traffic are some such factors.
Page Speed
The very first thing you need to check is the load speed of your competitor websites. Select the top ten websites on the SERP and put each URL on Google Page Speed Insights. It will let you know which one among them is the fastest loading website both on mobile and desktop. You should try to achieve top speed. The tool recommends the necessary changes you need to do to get a good page speed. Just follow the tips and you will end up with getting a fast-loading website.
On-Page Optimizations
A free tool like SEO Site Check Up can give you a lot of idea about the on-page factors that boost your competitors’ websites. Just put your website’s URL and check whether your website has proper heading tags, robots.txt file, sitemap.xml file, broken links, image alt texts, inline CSS, long HTML pages, favicon, JavaScript and CSS in minified format, long-chain redirects, URL Canonicalization, structured data, custom 404 pages, no-follow tags and more. Resolve if there’s an issue and try to improve your on-page score.
Backlinks
Backlinks have always been a major ranking signal. Getting links from high authority websites often leads to higher domain authority. Apart from that, it is one of the major sources of website traffic which is also necessary for SEO. Use a tool like AHREFS to find out the domains where your competitors hav acquired backlinks from and try to put your site’s links there. Always remember that authority of the website matters. So, do proper research on the domain that you are targeting and then move forward. Check the domain age and the number of traffic of a particular website before approaching. Lastly, do not look for backlinks from same domains. Try to increase the number of referring domains along with backlinks.
Website Traffic

Credits: https://gph.is/1UBjDHR
Website traffic is considered to be another important ranking factor. There are a lot of ways to bring traffic to your website. But among them, organic traffic greatly helps in ranking upliftment. It’s always difficult to get traffic organically with the target keywords at the beginning as there are a lot of high authority sites with huge domain authorities competing for the same keywords. Therefore, blogging can be an effective way to get traffic from search engines. What you need to keep in mind is that your blogs bring solutions to the user pain points. You should also look for what’s trending in your industry to create your stories. Make sure that the topics you choose, don’t have many search results but there’s a demand for quality content on those topics. Lastly, include enough information in your content and use all forms of media so that you can retain users on the blog page. It would eventually increase the ranking of your content and you will generate more organic traffic.
Useful Resource: Topic vs. Style: Which Comes First for Content Writing?
Another useful way to generate traffic to your website is social media engagement. But it’s quite difficult these days as most of the popular social media sites are encouraging paid promotions and thus, made a lot of restrictions when it comes to free marketing. Facebook can be a good example in the context as it restricts too many shares on groups. Even, posts are live only for a few hours on most of the channels. Therefore, creating communities, groups and pages based on entertainment or news and promoting your products and services there is an effective social media strategy. This really is a long-term process but there’s hardly any way of getting high engagement on social media overnight with free marketing.
Regular Content Creation
Google crawls and indexes websites for new content. And the frequency of crawling depends on the regularity of content creation and updates. Moreover, Google prefers what’s new on the web and therefore, recently published content always have a chance to get better visibility on the SERPs. Users also want to learn about the latest updates on a particular topic. Therefore, regular content creation on trending topics is very important. Update your content frequently and show the last modified date on the SERPs.
What Type of Businesses SEO Is Useful For?
These days, there’s hardly any company that can’t gain from Search Engine Optimization. Some get direct benefits and some indirectly. However, there are some businesses for which SEO can do wonders. Let’s take a look at them.
Businesses that are engaged in providing medical solutions like hospitals, dental treatment, emergency care clinics, etc, can gain huge benefits from SEO. Apart from creating a user-friendly website, they can post and promote highly informative articles that can improve their authority in the industry. They can also create how-to manuals to add value to customer’s lives and get more visibility in the SERPs.
Generally, when people are entangled in legal issues, they look for local counsels nearby and thus, appearing in local search is crucial for the law firms. A law practitioner can do a number of things to boost his/her local ranking. He/she can create a Google My Business listing and optimize it properly. They can also share legal information with users through blogs. The website can be optimized properly with the right sets of keywords. They can also get reviews on their Google and local business listings to boost their local search appearance.
Bars and restaurants can definitely make a huge killing through Search Engine Optimization, especially local SEO. People often search for restaurants and bars on Google Maps that suggest nearby places. Therefore, optimizing the website for local search and having a strong Google Maps presence can do wonders for this type of business. Getting reviews is also a big factor for restaurants and bars. According to a survey made by Bright Local, 60% of people claim that they read online reviews first before visiting a restaurant.
It’s been a long while that the real estate industry is getting benefitted from Search Engine Optimization. Moreover, there are some popular websites that promote real estate listings through paid promotions. Due to the emergence of these huge platforms, it’s quite difficult today for small real estate agents to rank for one or two-word phrase keywords. But, if they target local markets with long tailkeywords, they can achieve great outcomes.
Pet services are highly in demand at the local level. The keywords that are mostly used in this industry are grooming, supplies, walking, training and veterinarians. Like all other local services, valuable content and quality reviews are very important for pet services.
All kinds of emergency services have high search volume in Google as it is very common to make a Google search when the bathroom pipe in your home bursts and you are in need of immediate help. Therefore, local SEO is a prime source of leads for plumbers and electricians.
Tools and Software for SEO
These days, SEO is more of analyzing than doing repetitive tasks. And to do an in-depth analysis, you need tools like SEO Power Suit, Screaming Frog, Similar Web, BuzzSumo, Moz, Majestic, Mangools KWFinder, AHREFS, SEM Rush, Google Analytics, Google Search Console etc that are designed to help websites improve SEO ranking. With these tools you can research and target suitable keywords, identify the strength of competitors, audit your websites and solve the issues on your website if any, track the content that is performing well, focus more on the keywords that are generating more traffic to your website and more. Here, we will discuss about a few tools that are used by most of the webmasters and that can give you insightful data to help improve your SEO ranking.
Google Analytics

Google Analytics is one of the most essential free SEO tools. There are a lot of metrics offered by Google Analytics to understand the performance of your SEO strategy. Here, we will discuss some of the key metrics you need to check using this tool to strengthen your SEO strategy.
The very first thing you should check in Google Analytics is the traffic flow on your website with the passage of time and its nature. Whether the visitors are staying on your website or they are bouncing back. You can also learn about the location where most of the users are visiting from. It even lets you know about the device your visitors are using. The “Demographics” option shows you age and gender of the users. With the “Interest” option, you can come to know about the fields of interest of the users who are visiting your website. Another useful feature of the tool is “Acquisition” that discloses the traffic source of your audience. From it, you can learn whether you are getting users from the organic search, social media promotion or backlinks that you have created. You can learn about the pages that are getting clicks from each of the traffic sources by selecting “Landing Pages” in “Secondary Dimension”. Another way to learn about the most visited landing pages can be found in Behaviour > Site Content > Landing Pages. You can check the traffic sources of each landing page by selecting “Source/ Medium” in “Secondary Dimension”. This data will give you an idea about the landing pages that are performing well in the organic search and will help strategize your further SEO activities. You can also track the conversion on your website by setting up page visits, mail to link clicks and tel tag clicks.
Useful Resource: Ultimate Guide to Promote Your Website Using Google Analytics Data
Google Search Console

Another free tool from Google that is very popular with webmasters is Google Search Console. Though it takes a while to start showing data, the suggestions of the tool are very effective. It shows the number of clicks and impressions your popular landing pages have got in a particular period of time and highlights the search terms used to view or click on your landing page URL. This data is really helpful as you come to know the phrases for which you are ranking in the SERPs. The “URL Inspection” option is also helpful as it shows whether a particular URL has been indexed by Google and if there are some issues with the URL. With the “Mobile Usability” feature, you can come to know about the landing pages that might have some issues regarding mobile usability. It shows the errors that a particular URL has and suggests the ways to improve mobile appearance. You can also submit your sitemap.xml file to Google using this tool. It is very important as it lets Google learn about the important pages on your website and the ones that you don’t want to be indexed. There are several instances when you might find that some of your URLs have not been indexed by Google and thus, there’s no visibility of them in the SERPs. In such situations, you can submit the URL to Google Search Console and request for indexing.
AHREFS

AHREFS is one of the best tools for backlink analysis available in the market. It even identifies the backlinks that are not indexed by the crawlers of Google. You can also learn about the websites that have removed your site’s link. Apart from this, it helps you learn the keywords your website is ranking for. If you are new to SEO and want to create some effective backlinks in a short span of time, then the “link intersect” feature of AHREFS can prove to be most effective for you as it will show you the list of sites where your competitors have got backlinks from but you don’t. So, naturally, you end up creating backlinks from unique domains which is preferred by Google. It also comes with “domain comparison” option that helps you learn about the strength of your competitors and areas that you should improve. Apart from this, you can learn about the keywords that your competitors are ranking for and target those keywords in your SEO plan. Another great feature of this tool is “content explorer” that helps in identifying the content that is trending. Anchor texts have also been one of the major ranking factors for SEO. AHREFS lets you know the anchor texts used by your competitors to get the top ranking. Moreover, the tool comes with the option of creating projects that help you monitor your website’s presence on a regular basis. The “site audit” is another great feature of AHREFS. It checks the entire website and identifies all kinds of issues that might affect the overall ranking of the website. It crawls all internal pages and tells whether there are some broken URLs on your website. If there are some redirects, it checks the redirect chains and lets you learn about the longer ones. It also scans the titles, descriptions, tags and headings and identifies if there is an issue with them. If you have a slow loading website, it will analyze the issues and suggest ways to improve the page speed. Images have always been considered as a major part of SEO. AHREF checks each image on your website and highlights those that have no alt texts.
SEM Rush

SEM Rush is another popular paid tool. The most notable fact about the tool is that it suggests ways of SEO improvements apart from collecting data. All you have to do is to set a project here and connect your website with the tool. The tool also comes with the options to connect Google Search Console, Google Adwords, and social media channels so that you can get all the data in one place and make better strategies. The “Social Media Tracker” shows all your recent activities and engagements on popular social media channels and suggests you more effective ways by tracking your competitors. The “Site Audit” feature checks the health of your website and shows the pages with the issues and ways to solve them. With the “Brand Monitoring” option, you can check if your brand name is mentioned anywhere online. You will also have “Backlink Audit” feature that determines the backlink score of your website and identifies the toxic backlinks that might be hampering your SEO efforts. The “On-Page SEO Checker” option suggests beneficial ways for SEO improvements. It also identifies the top pages that are generating most volume of searches and gives suggestions to improve them by discovering more backlinking opportunities, content optimization techniques, technical issues and LSI keywords. The “Link Building Tool” finds more relevant websites where you can generate high-quality backlinks from. Apart from this, you can connect your email with the tool and send link building pitch directly to the site owners with this tool. To get more value out of this tool, you should connect your Google Search Console account with it. This will mark the websites from where you have already acquired backlinks. If you are going to create new content for your landing page, the “SEO Content Template” can make real wonders for you. All you need to do is to put the target keywords in the search bar and it will analyze the top ten competitors and suggest keywords, LSI keywords, titles, descriptions, ideal content length, potential backlinks, headings and more.
Web’s Best Resources for SEO
From the day of its inception, there’s been a lot of queries online regarding SEO. Naturally, the need for good SEO resources has always been felt. Thus, there’s a good number of SEO resources available online. Let’s learn about them.
Google Webmaster Central Blog
Get all the latest updates regarding crawling, indexing and ranking directly from Google at Webmaster Central Blog. Apart from this, the platform provides you with information about all the new features that are going to be included in SERPs. You can also get helpful reminders about Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and updates on Google Search Console.
Search Engine Land
One of the most popular SEO resources, the Search Engine Land was launched in 2007 with daily breaking news on all aspects of the search engine industry. The platform comes with tips, tactics and strategies from the industry experts to help aspiring webmasters grow.
Search Engine Journal
Founded in 2003, Search Engine Journal is another giant platform that shares industry news, analytical guides and insights for digital marketers. Apart from SEO, the website also focuses on PPC, Social Media and Content Marketing.
The Moz Blog
The Moz Blog was started by the popular SEO tool, Moz. It mainly covers topics like SEO, Social Media and Content Marketing. The platform shares regular updates and is very accurate about information. Moz’s Whiteboard Friday, generally an expert advice day is very popular with the webmasters as various large topics are discussed here in the easiest way possible.
Backlinko
Backlinko has become popular in a very short time. You can find a lot of blogs from backlinko into the top ten results with some very common search terms related to SEO. Typically, you will find monthly two to three detailed posts including actionable tactics and case studies from Backlinko.
Search Engine Watch
Launched in 1997, the platform holds the record of the longest-running online resource dedicated to digital marketing. It was launched by Danny Sullivan and generally speaks of SEO, Social Media, PPC and Content Marketing.
SEM Rush Blog
The platform is offered by the popular SEO tool, SEM Rush. It mainly focuses on content strategy, SEO, PPC and more. Here you can find an article post every day. The platform also welcomes guest posts.
Search Engine Roundtable
Published as a notebook in 2003 by Barry Schwartz, Search Engine Roundtable has been helping businesses from the very beginning. Here, you can find news, events, strategies, tips, and regular updates on search engines.
Yoast SEO Blog
Yoast SEO Blog is run by one of the most popular SEO plugins of WordPress, Yoast SEO. The resource is very popular with the bloggers who have blog sites, built using WordPress CMS.
The SEM Post
Though the platform was launched in 2014, it has acquired a good number of regular readers within this short span of time. It mainly focuses on comprehensive and in-depth case studies on updates along with profound analysis of the features of major search engines.
Common KPI’s of a Successful SEO Campaign
To determine the success of the Campaign, you need to set some KPIs. There can be various KPIs depending on the nature of your business and the audience you have targeted. But there are some common ones that are applicable to any SEO campaign. Let’s have a look at them.
- Targeted Organic Sessions
Though SEO is often associated with ranking, it’s not that getting the top rank solves the purpose of SEO. Getting relevant traffic is more important as this is what ultimately leads to conversion. And to get this done, the first thing you need to do is to target your keywords wisely.
It may happen, that the selected keywords merely have any search volume and competition. In such cases, you will definitely get a good rank but it’s of no use. Therefore, selecting the right keywords is definitely crucial before you start measuring SEO performance. You are also informed that the keyword selection hugely depends on which phase of marketing you are in. For example, if you have just started promoting a website, it’s better to go for keywords that have low to medium search competition as it would be difficult for you to beat the competitors who are in the SERPs from years and have high authority and traffic.
So, if the pages you have targeted with particular sets of keywords are able to generate organic traffic for you, you can definitely conclude that your SEO efforts are working. Try to find out, which keywords they are ranking for and optimize those pages with more relevant LSI keywords. It will eventually improve the ranking of pages and result in more relevant organic traffic.
2. Improved Keyword Ranking
If the above KPI is accomplished, you will definitely witness a ranking development as Google prefers landing pages having more click-through rate (CTR) in the SERPs. You can also use tools like SEM Rush or Rank Tracker to track the ranking changes. But always keep in mind that you must keep patience. Minor ranking changes can happen for a short while or after an algorithm update. But in the long run, you will witness the improvement.
3. Leads and Conversions
The first two KPIs are associated with attracting visitors to your website but the activities they make after landing on your website result in potential leads that can be converted into a sale. A lead can be a newsletter signup, contact form submission, phone call, registration for a webinar etc.
To measure the number of leads, you have to set goals and events in Google Analytics that can tell you from which device you are generating leads, what is the demography of your leads or which pages are generating more leads. Goal funnels can be created using Google Analytics to understand where people drop off and which areas of your website require further improvement.
Improvement in the number of leads does not only mean that your SEO efforts are successful but also it signifies that your users are taking desired actions. It’s an important KPI as it means that you understand your customers’ persona well. To improve the results of this KPI, emphasize more on the user experience of your website. Check whether your website is easy to navigate, the CTAs are prominent and clear, you have gained the users’ trust in their journey.
4. Referral Traffic
Referral traffic matters a lot because most of it comes from the backlinks created for your website. And link building is one of the major parts of SEO because of two reasons, traffic generation and domain authority improvement. So, if you are getting backlinks from relevant websites, you will definitely get traffic as well. Therefore, measuring traffic is also an important KPI for SEO.
5. Domain Authority
The domain authority of a website depends on various factors one of which is getting backlinks from high authority sites. Google counts a backlink as a vote and if you are getting links from good websites, it will be counted as a valuable vote. On the contrary, getting links from spammy or low authority websites would result in no improvement in domain authority. So, if you are on the right track, you will eventually witness an upliftment in domain authority. You can use a tool like SEM Rush to learn about the toxic score of your domain. It will highlight the websites where you shouldn’t have got backlinks from. To remove these backlinks, you can directly contact the site owners and ask them. You can also disavow those links from Google Search Console.
6. Bounce Rate
The bounce rate has a direct relation with the overall ranking of your website. A higher bounce rate often results in massive rankdrops as Google’s algorithm considers that people bounce because the content is not relevant or not informative enough to retain users on the landing page.
A bounce rate of 40 to 50 percent means that half of your potential customers have ended the session without taking any action. However, there’s no ideal bounce rate. It varies depending on the industry and niche.
Therefore, you should conduct a routine audit on your website, identify the pages that have a high bounce rate and make necessary changes to the pages. Conducting an A/B test can help you find the pages with a high bounce rate.
7. Pages/Session
Pages/Session means the number of pages a user visits in a particular session. It also includes repeated visits to a single page. But it is difficult to determine a good pages/session metric as it hugely depends on the structure of your website. For example, if you have a one-page website, then it’s quite natural to have a 1 page/session. But if it is a content-heavy website with useful information to help users or an eCommerce site where users often visit different pages to compare products, many Pages/Session is expected.
Along with other KPIs, Pages/Session is an important factor as it defines the value of your website and how users interact with it. Getting hundreds of visitors on your site is not effective until and unless they take actions on the landing page and browse through other valuable pages. Therefore, make sure that you have prominent CTA buttons even on the deep inner pages so that the users can be directed into your conversion funnel.
8. Average Session Duration
Session duration measures the average time spent by a visitor. The more in-depth and detailed content you have on your website, you can expect a longer session duration. It is an important KPI as it defines the quality of your web content and how well it can interact with your users. Therefore, focus on building quality content by understanding the query of your users and giving them proper solutions.
9. Top Exit Pages
An exit page is the last page visited by a user before ending the session. But it’s not that all the exit pages leave a negative impact on the users. Your top exit page can also be a thank you page that is left by a user after the successful completion of the sales funnel.
Role of Website Design in SEO
In the beginning, SEO was all about creating backlinks with keyword-based anchor texts. Webmasters hardly emphasized the user experience part. But as Google grew smarter, and it started giving priority to the users, adding value to the content rather than the activities are done to promote the content became the most essential SEO factor.
And with it, the way you present the content gets emphasized. Naturally, the design of the website joins the game. Google started measuring, how satisfied the visitors are while interacting with the content of a web page. Are they staying on it and taking actions or bouncing back right after they visit? Interactions with the numbers of pages started getting importance as it defines the overall presentation of the website. Along with this, the load speed became an integral part of website design as heavily designed websites take too long to load and it affects user experience a lot.
In addition to the user experience, building a clearly defined structure of a website also got importance because it is necessary for Google to understand what your website is all about to make your content visible to the users. And that’s why you need to create a proper sitemap.xml file.
You would not like to make all the pages on your website visible to the audience for example login page, or payment page. This is when a proper set of robots.txt file is needed. It instructs the search engines which pages to crawl and not to crawl. To make content easily readable to the search engines, the need for clearly defined codes also emerged and that’s why website designs with less code clutter have become an important factor today.
Another important web design metrics for SEO is cross-browser compatibility. Make sure that your website opens properly in all browsers as it may leave a huge impact on the bounce rate of your website. You should also be careful while using flash elements on your website as they are often ignored by the search engines. Moreover, using flash too many times cause distraction to the users and it may eventually lead to an increase of bounce rate.
Search Engine bots cannot read JavaScript files properly and that leads to crawl errors and improper indexation. In fact, JavaScript files don’t work perfectly on mobile devices. So, if you are going to use JavaScript on your website, try not use it extensively as it may cause crawling issues and improper indexation.
Conclusion
There’s nothing absolute in SEO. Search engine algorithms change frequently and optimization tactics evolve in response to those changes. So, getting started from the basics is always recommended to understand the evolution of the industry and make future predictions. Then do an in-depth keyword analysis and outreach to other websites to link to you. These three steps are the basics of SEO.
Hope you enjoyed the suggestions. Follow us regularly for more exciting updates on Search Engine Optimization.
Image/Video Credits: https://www.google.com/search/howsearchworks/
